- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts
- PMC6742548

Fine-Tuning of PGC1α Expression Regulates Cardiac Function and Longevity
Xudong Zhu
1Institute of Aging Research, Hangzhou Normal University School of Medicine, 1378 Wenyixi Road, Hangzhou
Weiyan Shen
2Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine of Ministry of Education, Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory, Institute of Aging and Regenerative Medicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou
Ke Yao
3School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Hu Wang
1Institute of Aging Research, Hangzhou Normal University School of Medicine, 1378 Wenyixi Road, Hangzhou
2Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine of Ministry of Education, Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory, Institute of Aging and Regenerative Medicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou
Bo Liu
2Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine of Ministry of Education, Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory, Institute of Aging and Regenerative Medicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou
Tangliang Li
1Institute of Aging Research, Hangzhou Normal University School of Medicine, 1378 Wenyixi Road, Hangzhou
Lijuan Song
4Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou
Daojun Diao
2Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine of Ministry of Education, Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory, Institute of Aging and Regenerative Medicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou
Genxiang Mao
5Zhejiang Provincial Key Lab of Geriatrics & Geriatrics Research Institute of Zhejiang Province, Department of Geriatrics, Zhejiang Hospital, Hangzhou
Ping Huang
6Shanghai Key Laboratory of Forensic Medicine, Shanghai Forensic Service Platform, Institute of Forensic Sciences, Ministry of Justice, Shanghai
Chengtao Li
6Shanghai Key Laboratory of Forensic Medicine, Shanghai Forensic Service Platform, Institute of Forensic Sciences, Ministry of Justice, Shanghai
Hongbo Zhang
7Laboratory for Integrative and Systems Physiology, Institute of Bioengineering, École Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne, Lausanne
Yejun Zou
8Synthetic Biology and Biotechnology Laboratory, State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center for Biomanufacturing Technology, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai
Yugang Qiu
9School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Weifang Medical University, Weifang
Yuzheng Zhao
8Synthetic Biology and Biotechnology Laboratory, State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center for Biomanufacturing Technology, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai
Wengong Wang
10Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Beijing Key Laboratory of Protein Posttranslational Modifications and Cell Function, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing
Yi Yang
8Synthetic Biology and Biotechnology Laboratory, State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center for Biomanufacturing Technology, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai
Zeping Hu
3School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Johan Auwerx
7Laboratory for Integrative and Systems Physiology, Institute of Bioengineering, École Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne, Lausanne
Joseph Loscalzo
11Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Dept. Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston
Yong Zhou
12Beijing Sanbo Brain Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing.
Zhenyu Ju
2Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine of Ministry of Education, Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory, Institute of Aging and Regenerative Medicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou
Associated Data
- Supplementary Materials
- 315529 Online Supplement.GUID: 2B052C94-A10B-4EBA-B8CC-2CF7C773C6BE315529 Preclinical checklist.GUID: 2A0BFDA4-87B9-4580-9B06-05108C40B8DD
Abstract
Rationale:
PGC1α represents an attractive target interfering bioenergetics and mitochondrial homeostasis, yet multiple attempts have failed to upregulate PGC1α expression as a therapy, for instance, causing cardiomyopathy.
Objective:
To determine whether a fine-tuning of PGC1α expression is essential for cardiac homeostasis in a context-dependent manner.
Methods and Results:
Moderate cardiac-specific PGC1α overexpression through a ROSA26 locus knock-in strategy was utilized in wild-type (WT) mice and in a third generation of telomerase-deficient (G3Terc−/−, hereafter as G3) mouse model, respectively. Ultrastructure, mitochondrial stress, echocardiographic, and a variety of biological approaches were applied to assess mitochondrial physiology and cardiac function. While WT mice showed a relatively consistent PGC1α expression from 3-month-old to 12-month-old, age-matched G3 mice exhibited declined PGC1α expression and compromised mitochondrial function. Cardiac-specific overexpression of PGC1α (PGC1αOE) promoted mitochondrial and cardiac function in 3-month old WT mice but accelerated cardiac aging and significantly shortened lifespan in 12-month old WT mice due to increased mitochondrial damage and ROS insult. In contrast, cardiac-specific PGC1α knock-in in G3 (G3 PGC1αOE) mice restored mitochondrial homeostasis and attenuated senescence-associated secretory phenotypes, thereby preserving cardiac performance with age and extending health span. Mechanistically, age-dependent defect in mitophagy is associated with accumulation of damaged mitochondria that leads to cardiac impairment and premature death in 12-month old WT PGC1αOE mice. Whereas in the context of telomere dysfunction, PGC1α induction replenished energy supply through restoring the compromised mitochondrial biogenesis and thus is beneficial to old G3 heart.
Conclusions:
Fine-tuning the expression of PGC1α is crucial for the cardiac homeostasis, as the balance between mitochondrial biogenesis and clearance is vital for regulating mitochondrial function and homeostasis. These results reinforce the importance of carefully evaluating the PGC1α-boosting strategies in a context-dependent manner to facilitate clinical translation of novel cardioprotective therapies.
INTRODUCTION
Cardiac degeneration and cardiovascular diseases remain intricate threats to health and longevity. Unlike other high-turnover tissues, renascence of cardiomyocytes cannot be realized due to the lack of adult cardiac stem cells in the post-mitotic heart1-4. Instead, mitochondrial functional integrity plays an important role in maintaining cardiac homeostasis and especially, during aging. A great body of work has shown that cardiac aging, including pathologically premature aging, is closely related to mitochondrial damage5-9. Although the causal relationship between mitochondrial compromise and cardiac aging is still inconclusive, a consensus has been reached that maintaining the mitochondrial fitness is the key to attenuate age-dependent cardiac degeneration. However, the precise mechanism of mitochondrial quality control during cardiac aging remain to be elucidated.
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC1α) plays a prominent role in regulating mitochondrial biogenesis, oxidative phosphorylation, energy metabolism, oxidative stress response, and other functions across a wide range of tissues10. Clinical significance of PGC1α lies in the derangements in PGC1α level as well as Ppargc1a polymorphisms, and their associations with the clinical expression of diseases, e.g. diabetes11, 12, cancer13-15, and cardiomyopathy16-18. The regulatory effects of PGC1α in pathogenesis have been manifested in different animal models, however, attempts to boost PGC1α level as a therapeutic strategy often meet contradictory results. For instance, PGC1α knock-out in muscle led to reduced endurance capacity and exhibited fiber damage19, while transgenic expression of PGC1α increased the content of slow-twitch muscle fibers, concurrent with enhanced exercise performance and peak oxygen uptake, but causing insulin resistance in animals fed high fat diet20. In heart, PGC1α null mice did not present a baseline phenotype but worsened stress response21. Conversely, high level overexpression of PGC1α caused cardiomyopathy10, 22, 23. Thus, these results implicate that regulation of PGC1α dosage is of particular importance and context-dependent.
Age-associated telomere attrition represents one intrinsic driver of aging, contributing to the dysfunction of multiple organs and the occurrence of age-related diseases24. The telomerase knockout (Terc−/−) mice have been utilized as a sophisticated and reliable aging model that resembles human aging process with chronic telomere dysfunction. Notably, heart degeneration in mice with shortened telomeres has been linked to p53 mediated suppression of PGC1α and consequent mitochondrial dysfunction9. Accordingly, mice with dysfunctional mitochondria also exhibited a premature aging phenotype accompanied by a distinct senescence-associated secretory phenotype25. In this scenario, it is worth constructing a mouse model of mild PGC1α knock-in and deciphering whether cardiac PGC1α knock-in causes distinct biological effects in telomere-intact and telomere dysfunctional mice, respectively, in which telomere dysfunctional heart has lower PGC1α expression in comparison to the telomere-intact counterpart.
To address the questions above, we utilized a ROSA26 locus knock-in approach to mildly overexpress PGC1α specifically in cardiomyocytes of wild-type (WT) and third generation of Terc−/− (G3) mice. Functional characterizations of the two cohorts revealed that PGC1α promoted mitochondrial and cardiac function in 3-month old WT and G3 mice but accelerated cardiac aging and significantly shortened lifespan in 12-month old WT mice partially due to age-dependent defect in mitophagy. In contrast, in the context of telomere dysfunction, PGC1α induction replenished energy supply through restoring the compromised mitochondrial biogenesis and thus was beneficial to old G3 heart. Collectively, our results highlight the importance of fine-tuning PGC1α expression to maintain mitochondrial functionality and cardiac homeostasis during aging.
METHODS
All data from these experiments are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Animals.
All studies with mice were approved by the Institutional Animal Use and Care Committee of Hangzhou Normal University. C57BL/6J mice (refer as ‘wild type’ or ‘WT’) were purchased from the Laboratory Animal Center of Hangzhou Normal University. Cardiac specific alpha myosin heavy chain Cre recombinase (αMHC Cre+/−) mice, Terc+/− (T+/−) heterozygous and Terc−/− (T−/−) telomere-deficient mice, PGC1αF/+ mice were all backcrossed for 10 generations onto a C57/BL6 background. The PGC1αF/+ mice were intercrossed with αMHC Cre+/− mice to generate PGC1αF/+-αMHC Cre+/− (WT PGC1αOE) mice, which were further crossed with T+/− mice to generate T+/− PGC1αOE mice. The T+/− PGC1αOE mice and T+/− mice were further crossed to generate first generation of telomere-deficient mice (G1Terc−/− mice) or G1Terc−/− PGC1αOE mice, which were crossed successively to produce the third-generation G3Terc−/−PGC1αOE (G3 PGC1αOE) and control littermates (i.e. G3, αMHC Cre+/−G3, and PGC1αF/+G3 mice). No developmental or survival differences were found among the control littermates examined, thus these three groups all designated ‘G3’ hereafter.
Electron microscopy.
Heart samples were fixed in 20-fold volumes of 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1M PBS solution for 48 hours, followed by 3 times of rinse in 0.1M PBS for 10 minutes each, then fix in 1% OsO4 for 1 hour at room temperature and rinse in distilled H2O for 3 times. The samples then were transferred into 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes containing 2% uranyl acetate for 30 min, followed by gradient rinse in 50%, 70%, 90%, 100% ethanol for 10 minutes, and 2 times of 100% acetone rinse for 15 minutes. The specimens were infiltrated, embedded, polymerized, sectioned, and stained as previously described26.
Statistics.
Statistical analyses were performed using Prism 7 (GraphPad Software Inc.). Unpaired student’s t-test (two-tailed) was used to compare two normally distributed data sets. One-way ANOVA was used, where appropriate, to compare more than two data sets. A P value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. All data were shown as mean ± standard error of mean.
For further information of the methodology please see the Supplemental Material online.
RESULTS
Cardiac deterioration in 12-month-old G3 mice and 24-month-old WT mice.
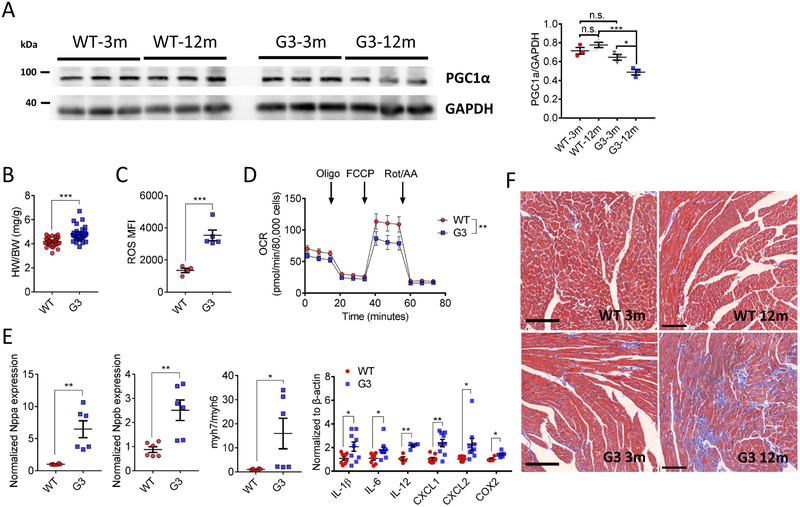
Previous study demonstrated that late generation of telomerase-deficient mice developed an impaired cardiac function due to repressed PGC1α expression9. Indeed, distinct PGC1α expression patterns were found between WT and G3 hearts during aging. In contrast to relatively stable PGC1α level between 3-month-old and 12-month-old WT hearts, a significant reduced PGC1α expression (P < 0.05) was seen in 12-month-old G3 heart versus its young counterpart (Figure 1A), while WT hearts exhibited a decreased PGC1α level at 24-month-old (P < 0.05, Online Figure I), coincided with augmented reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (P < 0.01, Online Figure I), increased myh7-to-myh6 ratio (P < 0.001, Online Figure I), and hypertropic cardiac dysfunction (P < 0.01, Online Figure I-). Notably, 12-month-old G3 heart exhibited increased heart-weight to body-weight ratio (P < 0.001, Figure 1B) and ROS production (P < 0.001, Figure 1C) versus that of age-matched WT heart. The functional defects of G3 heart was further substantiated by impaired mitochondrial respiration (Figure 1D), concurrent with augmented cardiac stress indices and elevated inflammatory related gene expression (Figure 1E). In line with this, we documented a significant fibrosis (Figure 1F) in 12-month-old G3 heart compared with WT heart. Intriguingly, we also observed an increased NADH-to-NAD+ ratio (P < 0.01, Online Figure II) as well as more protein aggregates (Online Figure II) in aged G3 cardiomyocytes. These data indicate that downregulation of PGC1α is associated with accelerated cardiac deterioration in aged WT and G3 mice.
A, Left ventricular tissue lysates from wild-type (WT) and G3Terc−/− (G3) mice at the age of 3-month-old and 12-month-old, respectively, were subjected to Western blotting with the PGC1α antibody. Relative PGC1α level was calculated by normalization to GAPDH (right panel). n = 3 for each group. One-way ANOVA followed by Sidak's post-hoc test. n.s. no significance, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. B, Increased heart weight-to-body weight ratio (HW/BW) was found in 12-month-old G3 mice. WT: n = 34; G3: n = 31. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). ***P < 0.001. C, Increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in 12-month-old G3 cardiomyocytes versus that of WT mice. WT: n = 4; G3: n = 5. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). ***P < 0.001. D, Mitochondrial respiration was measured in primary isolated cardiomyocytes from 12-month-old WT (red circle) and G3 (blue circle) mice. Oxygen consumption rates (OCR) are presented as pmol/min per 80,000 cells. Oligo, oligomycin; FCCP, carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone; Rot/AA, rotenone/antimycin A. n = 4 for each group in triplicate. Two-way ANOVA. **P < 0.01. E, Cardiac stress and inflammation-related gene expression were upregulated in 12-month-old G3 hearts. n = 6 for each group, except for inflammatory panel (n = 4-9 for each group). Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. F, Representative images of Masson’s trichrome staining in 3-month-old and 12-month-old WT and G3 hearts. n = 3-4 for each group. Bar = 100 μm. Data were shown as mean ± standard error of mean.
PGC1αOE improves mitochondrial and cardiac function in young WT and G3 hearts.
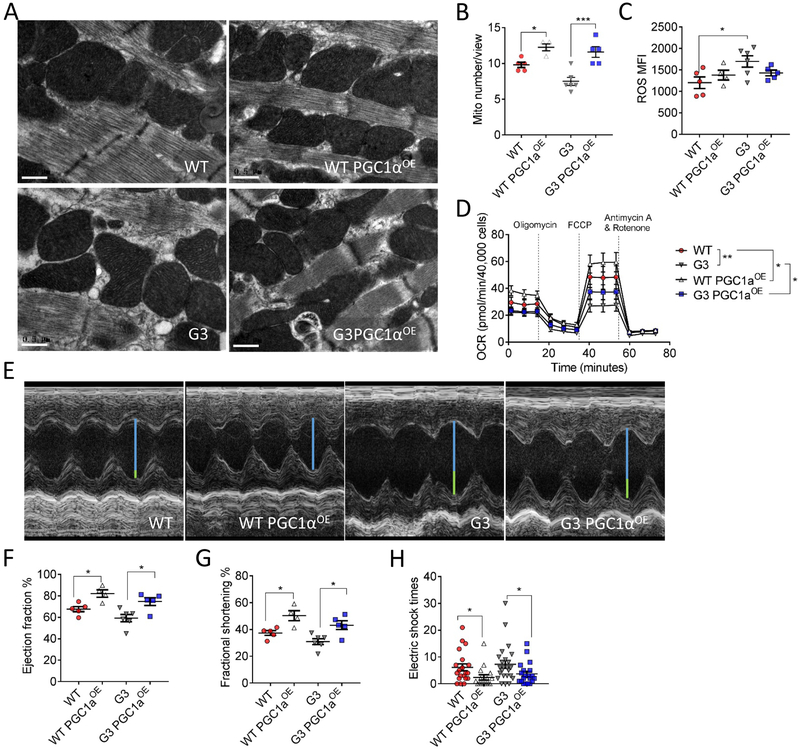
The above profiles prompted assessment of whether elevating PGC1α level could attenuate aging-dependent structural and functional deterioration in old WT and G3 heart. Given that previous studies have shown cardiomyopathy could be induced via a boost of PGC1α expression22, 23, it is of particular interest to compare the biological effect of mild cardiac-specific PGC1α overexpression between WT and telomere dysfunctional mice within a physiological range. To this end, we engineered a cardiac-specific PGC1α knock-in WT (WT PGC1αOE) and telomere-deficient mouse (G3 PGC1αOE), respectively, where PGC1α was under transcriptional control of the endogenous Rosa26 promoter (Online Figure III). This strategy moderately increased PGC1α expression in WT and G3 hearts (Online Figure III), and electron microscopy (Figure 2A and and2B)2B) and mitochondrial staining (Online Figure IV) revealed that cardiac PGC1α knock-in increased mitochondrial mass with normal mitochondrial morphology in both 3-month-old WT and G3 hearts, although G3 hearts exhibited a slightly higher ROS production (Figure 2C). In line with this, a significant enhanced basal and maximal oxygen consumption rate (OCR) (Figure 2D) was found in both WT PGC1αOE and G3 PGC1αOE cardiomyocytes versus their respective counterparts. Interestingly, such moderate elevation of PGC1α expression is sufficient to improve cardiac function (Figure 2E--G)G) and exercise tolerance (Figure 2H). These results demonstrate that in young stage, moderate PGC1αOE is favorable to enhance mitochondrial biogenesis and function without causing adverse effect seen in previous PGC1αOE models.
Cardiac-specific PGC1α expression improves mitochondrial and cardiac function in young WT and G3 hearts. A, Representative transmission electron microscopy images of 3-month-old WT, WT PGC1αOE, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE hearts. Bar = 0.5 μm. 11500x magnification. B, Quantification of mitochondrial number per view of transmission electron microscopy images from 3-month-old WT, WT PGC1αOE, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE hearts. WT: n = 5; WT PGC1αOE: n = 4; G3: n = 6; and G3 PGC1αOE: n = 5. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. C, ROS production in isolated cardiomyocytes of 3-month-old WT, WT PGC1αOE, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice. *P < 0.05. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. D, PGC1αOE leads to an enhanced mitochondrial respiration in both WT and G3 cardiomyocytes. OCR are presented as pmol/min per 40,000 cells. n = 4 for each group in quadruplicate. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Two-way ANOVA. E, Representative echocardiographic images of 3-month-old WT, WT PGC1αOE, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice. Blue line indicates the left ventricular internal diameter end diastole of WT PGC1αOE mice, and the connected green lines indicate the enlarged diameter in WT, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice versus that of WT PGC1αOE mice. F and G, Measurements of ejection fraction (F, n = 4-6 per genotype) and fractional shortening (G, n = 4-6 per genotype) in 3-month old WT, WT PGC1αOE, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice. *P < 0.05. One-way ANOVA followed by the Sidak’s post-hoc test. H, Exercise-tolerance test of 3-month old WT, WT PGC1αOE, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice. n = 4-6 per genotype. Mice were subjected to treadmill exercise once a day for continuous four days. *P < 0.05. One-way ANOVA followed by the Sidak’s post-hoc test. Data were shown as mean ± standard error of mean.
Deteriorated cardiac function and reduced lifespan in WT PGC1αOE mice.
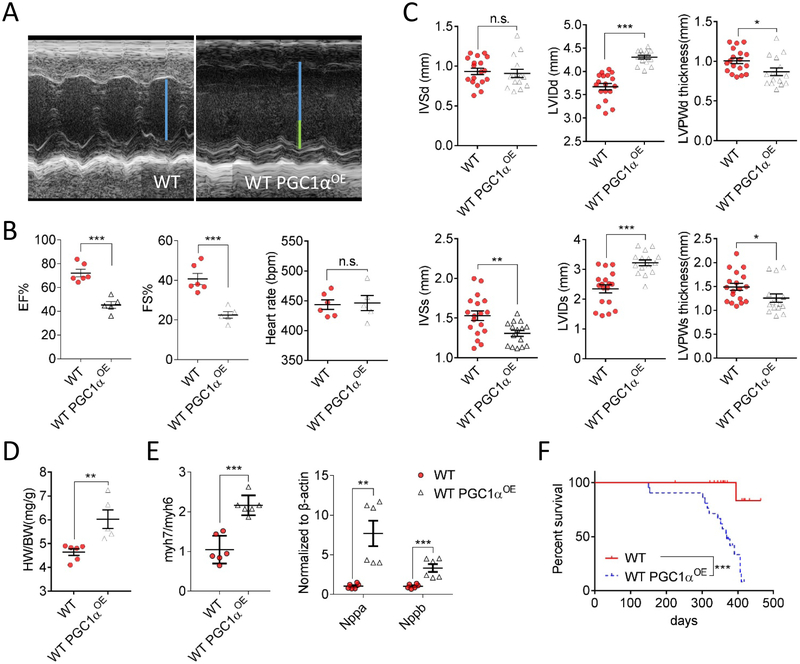
We next examined whether aforementioned salutary effects in young mice can maintain to an old age, which is crucial for cardiac homeostasis since the abundant mitochondria residing in the heart accumulate more damage during aging. We first subjected WT and WT PGC1αOE mice to echocardiographic assessment (Figure 3A). Surprisingly, 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE mice exhibited an accelerated cardiac dysfunction as evidenced by lowered eject fraction and fraction shortening (Figure 3B), concurrent with thinner systolic interventricular septum diameter and left ventricular posterior wall thickness, while a dilated left ventricular internal dimension (Figure 3C). These altered parameters echoed with a significant increase in heart weight-to-body weight ratio (P < 0.01, Figure 3D) as well as the cardiac stress-related gene expressions (Figure 3E). The survival analysis indicated that a dramatically shortened lifespan occurred in WT PGC1αOE mice with the median survival of only one year (P < 0.001, Figure 3F).
A, Representative echocardiographic images of 12-month-old WT and WT PGC1αOE mice. Blue line indicates the left ventricular internal diameter end diastole of WT mice, and the connected green lines indicate the enlarged diameter in WT PGC1αOE mice versus that of WT PGC1αOE mice. B, Measurements of ejection fraction (EF%), fractional shortening (FS%), and heart rate in 12-month old WT and WT PGC1αOE mice. WT: n = 6; WT PGC1αOE: n = 5. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). n.s. no significance, ***P < 0.001. C, Left ventricle interventricular septal end diastole (IVSd, top) and end systole (IVSs, bottom); left ventricular internal diameter end diastole (LVIDd, top) and end systole (LVIDs, bottom); and left ventricular posterior wall thickness end diastole (LVPWd, top) and end systole (LVPWs, bottom) from 12-month-old WT and WT PGC1αOE mice. WT: n = 6; WT PGC1αOE: n = 5. Measurements were done in triplicate for each mouse. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). n.s. no significance, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. D, Increased heart weight-to-body weight ratio (HW/BW) was found in 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE mice. WT: n = 6; WT PGC1αOE: n = 5. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). **P < 0.01. E, Cardiac stress-related gene expression were upregulated in 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE left ventricular tissues. n = 6 for each group. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. F, Kaplan-Meier survival curves of WT and WT PGC1αOE mice with Mantel-Cox test. n = 21 per genotype. ***P < 0.001. Data were shown as mean ± standard error of mean.
Deteriorated mitochondrial function in WT PGC1αOE heart during aging.
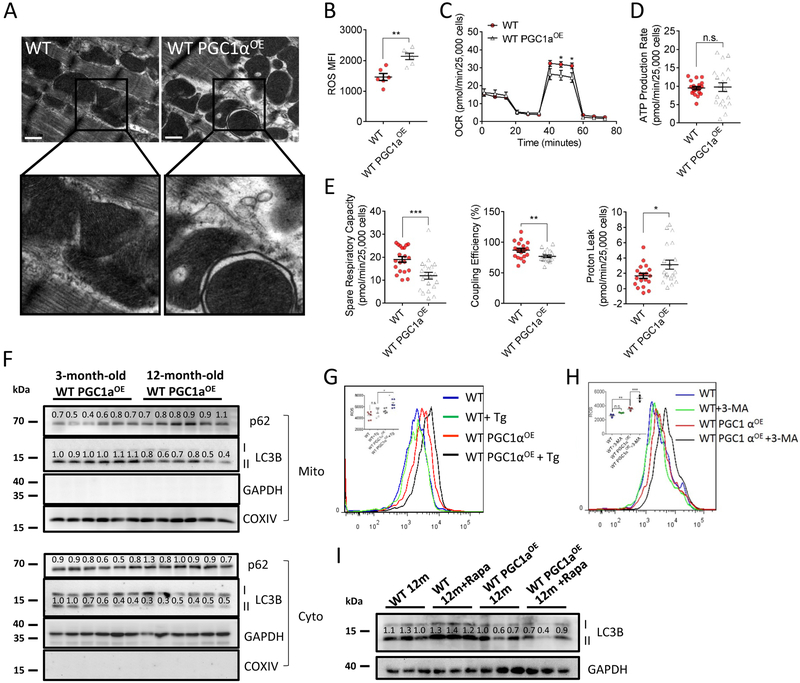
We investigated the mechanism of PGC1αOE-induced cardiac dysfunction and premature death in aged mice. Electron microscopy analyses revealed that 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE heart contained a portion of distorted mitochondria, with enlarged cristae compartments in comparison to that of the age-matched WT mice (Figure 4A). Mitochondrial ROS level was also significantly increased in 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE cardiomyocytes (P < 0.01, Figure 4B), accompanied by a reduced oxygen consumption rate (OCR) (Figure 4C), although the ATP production was unchanged (Figure 4D). In line with these findings, spare respiration capacity and coupling efficiency were both decreased, while an augmented proton leak was seen in 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE cardiomyocytes (Figure 4E). These mitochondrial defects linked to reduced autophagy and citrate cycle activity in 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE heart as analyzed by RNA sequencing (Online Figure V). Indeed, Western blotting of autophagy-related proteins, e.g. p62 and LC3b-II, confirmed a reduced mitochondrial autophagy (aka mitophagy) in old WT PGC1αOE heart versus young counterpart (Figure 4F). To verify whether mitophagy is required to maintain the mitochondrial fitness in WT PGC1αOE heart, we utilized thapsigargin (Tg), an autophagy blocker27, to treat 3-month-old WT and WT PGC1αOE cardiomyocytes and found a significant increased ROS production in WT PGC1αOE, but not in WT cardiomyocytes (Figure 4G). Similar finding was seen using another autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA) (Figure 4H). In line with this, an eight-week 3-MA treatment significantly accelerated cardiac dysfunction in WT PGC1aOE mice, but not in WT controls (Online Figure VI). In vitro mitochondrial functional characterization also confirmed that 3-MA treatment lowered ATP production in 3-month-old WT PGC1aOE cardiomyocytes, while minor changes were observed in WT control cardiomyocytes (Online Figure VI), further strengthening the causality linking mitochondrial alterations with cardiac dysfunction in WT PGC1aOE mice. In addition, given that rapamycin (Rapa) has shown the ability to induce mitophagy28, we further explored the mitophagic capacity by incubating 12-month-old cardiomyocytes with 200 nM rapamycin. While rapamycin-treated WT cardiomyocytes showed a positive response after 12h incubation, WT PGC1αOE cardiomyocytes failed to stimulate, or even inhibition of autophagy to some extent (Figure 4I). Taken together, these findings suggest that impaired mitophagic capacity in old WT PGC1αOE heart may account for its cardiac compromise and premature death.
A, Representative transmission electron microscopy images of 12-month-old WT and WT PGC1αOE hearts. Bar = 0.5 μm. 11500x magnification. B, ROS production in isolated cardiomyocytes of 12-month-old WT and WT PGC1αOE mice. n = 6 for each. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). **P < 0.01. C, WT PGC1αOE cardiomyocytes exhibited a lowered mitochondrial respiration in comparison to that of WT cardiomyocytes at the age of 12-month-old. OCR are presented as pmol/min per 25,000 cells. n = 5 for each group in quadruplicate. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). *P < 0.05. D, No significant change of ATP level was found in 12-month-old WT and WT PGC1αOE cardiomyocytes. Data are presented as pmol/min per 25,000 cells. n = 5 for each group in quadruplicate. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed), n.s. no significance. E, Decreased spare respiratory capacity and coupling efficiency, while increased proton leak were seen in WT PGC1αOE cardiomyocytes in comparison to that of WT cardiomyocytes at the age of 12-month-old. Data are presented as pmol/min per 25,000 cells. n = 5 for each group in quadruplicate. Unpaired t-test (two-tailed). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. F, Decreased mitophagy was found in 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE heart versus that of 3-month-old counterpart. p62 and LC3B I/II antibodies were used as autophagic markers. GAPDH was used for cytosol (cyto) internal control and COX IV for mitochondria, respectively. n = 6 for each group. G&H, Flow cytometry analysis indicated a significant increased ROS production in 3-month-old WT PGC1αOE, but not in WT cardiomyocytes, upon one-hour incubation of 1.5 μM thapsigargin (Tg, G, n = 6 for each group.) or 1 mM 3-methyladenine (3-MA, H, n = 3 for each group.) in comparison to the controls. One-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. n.s. no significance, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. I, Reduced mitophagic capacity was found in 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE cariomyocytes versus that of WT cardiomyocytes upon 12-hour incubation of 200 nM rapamycin (Rapa). n = 3 for each group. Data were shown as mean ± standard error of mean.
Cardiac PGC1α induction preserves cardiac function and extends health span in G3 mice.
In contrast to the deteriorating effect of PGC1αOE in 12-month-old WT mice, a normalized heart weight-to-body weight ratio was seen in G3 PGC1αOE mice (Figure 5A), along with the PGC1α expression restored to a level that comparable to WT mice (Online Figure VII). We next subjected aged G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice to echocardiographic assessment. G3 PGC1αOE mice exhibited an improved cardiac function compared with G3 mice (Figure 5B), including enhanced left ventricular ejection fraction and fraction shortening (Figure 5C), as well as reduced left ventricular dilatation and LVPW thickness (Figure 5D). Consistently, analyses of RNA sequencing results revealed down-regulation of dilated cardiomyopathy-related pathways after cardiac PGC1α induction (Online Figure VIII and Online Table I). Despite the absence of proliferative or apoptotic changes in all heart samples examined, a spectrum of cardiac degenerative markers were significantly declined in G3 PGC1αOE hearts (Figure 5E), suggesting PGC1α attenuated cardiac dysfunction of G3 mice during aging. Indeed, aged (~350-day old) G3 mice displayed many typical degenerative indications, such as senile plaques, kyphosis, hair loss (Online Figure IX) and accelerated body mass loss (Online Figure IX), while age-matched G3 PGC1αOE mice appeared healthier with an overall improved fitness. Indeed, a 15-minute run test demonstrated that aged G3 PGC1αOE mice were as exercise-tolerant as WT mice, both significantly better than G3 mice (Figure 5F). Consistent with above findings, a highly significant increase in median lifespan was observed in G3 PGC1αOE cohort compared with that of G3 cohort (Figure 5G and Online Figure X), indicating that cardiac PGC1α knock-in extends health span in G3 mice.
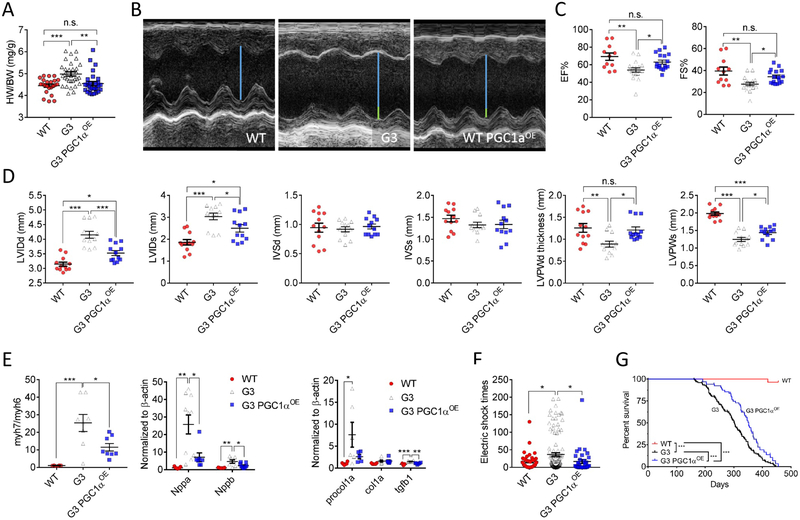
A, Normalized heart weight-to-body weight ratio (HW/BW) was found in 12-month-old G3 PGC1αOE mice. WT: n = 23; G3: n = 31; G3 PGC1αOE: n = 29. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. n.s. no significance, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. B, Representative echocardiographic images of 12-month-old WT, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice. Blue line indicates the left ventricular internal diameter end diastole of WT mice, and the connected green lines indicate the enlarged diameter in G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice versus that of WT mice. C, Measurements of ejection fraction (EF%) and fractional shortening (FS%), and heart rate in 12-month old WT, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice. WT: n = 11; G3: n = 18; G3 PGC1αOE: n = 17. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. n.s. no significance, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. D, Left ventricle interventricular septal end diastole (IVSd) and end systole (IVSs); left ventricular internal diameter end diastole (LVIDd) and end systole (LVIDs); and left ventricular posterior wall thickness end diastole (LVPWd) and end systole (LVPWs) from 12-month-old WT, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice. n = 4 for each genotype. Measurements were done in triplicate for each mouse. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. n.s. no significance, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. E, Cardiac stress and fibrosis-related gene expression were attenuated in 12-month-old G3 PGC1αOE hearts. n = 5-10 for each group. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. F, Exercise-tolerance test of 12-month old WT, G3, and G3 PGC1αOE mice. n = 6-12 per genotype. Mice were subjected to treadmill exercise once a day for continuous six days. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. n.s. no significance, *P < 0.05. G, Kaplan-Meier survival curves of WT, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice with Mantel-Cox test. WT: n = 27; G3: n = 147; G3 PGC1αOE: n = 66. Data were shown as mean ± standard error of mean.
Sustained mitochondrial function and calmed inflammation in G3 PGC1αOE mice during aging.
To further explore the underlying mechanism of PGC1αOE-mediated beneficial effects in G3 mice, we performed additional analyses. RNA sequencing of aged G3 and G3 PGC1αOE hearts using differential gene expression analysis revealed an up-regulation of oxidative phosphorylation pathways in comparison to G3 hearts (Online Figure XI and Online Table I). Moreover, transmission electron microscopy showed reinstated mitochondrial morphology and restored mtDNA content in aged G3 PGC1αOE hearts (Figure 6A and and6B),6B), concurrent with improved mitochondrial respiration (Figure 6C), lowered ROS production (Figure 6D), and calmed inflammatory cytokine secretion (Figure 6E--G).G). These results suggest that PGC1α knock-in ameliorates telomere deficiency-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Altogether, these data reinforce that therapeutic regulation of PGC1α in cardiac aging should aim at achieving moderate induction of PGC1α within a therapeutically beneficial window.
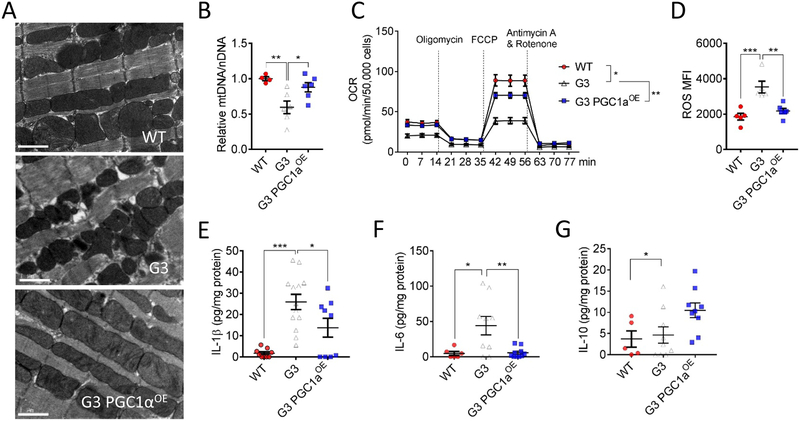
A, Representative transmission electron microscopy images of 10-month-old WT, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE cardiomyoctes. Bar = 1 μm. 8300x magnification. B, PGC1α induction normalized mtDNA-to-nDNA ratio in 10-month-old G3 hearts to that of WT hearts. n = 4-6 in each group. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. C, Mitochondrial respiration measured in primary cardiomyocytes from 10-month-old WT, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice. Oxygen consumption rates (OCR) are presented as pmol/min per 50,000 cells. Two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. D, PGC1α induction reduced ROS production in 10-month-old G3 cardiomyocytes. n = 5-6 in each group. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. E-G, Quantification of cardiac IL-1β (E), IL-6 (F), and IL-10 (G) in 10-month-old WT, G3 and G3 PGC1αOE mice. n = 5-13 in each genotype. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data were shown as mean ± standard error of mean.
DISCUSSION
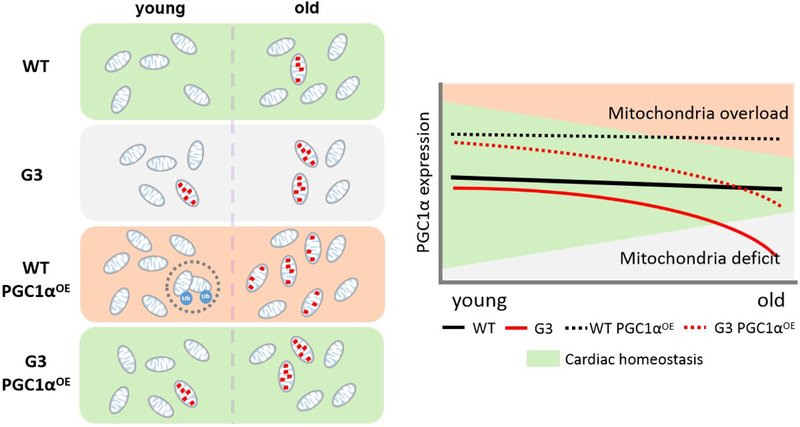
Here we document distinct biological effects of cardiac-specific PGC1α overexpression in WT and a later generation of telomere-deficient mice, respectively, in which telomere dysfunctional heart exhibits a lower basal PGC1α expression in comparison to the telomere-intact counterpart. Notably, we found accelerated cardiac degeneration and significantly shortened lifespan in WT PGC1αOE mice, while a favorable longevity-extending effect in G3 PGC1αOE mice despite the fact that the PGC1α knock-in was restricted to the heart. We believe that the contrasting consequence in our models is, at least partially due to the dose effect of PGC1α on tuning mitochondrial biogenesis and clearance. That is, full functional mitochondrial quality control is engaged in WT heart of normal PGC1α expression. In aged G3 heart of low PGC1α expression, however, energy deficit occurs due to the fact that damaged mitochondria exceed mitochondrial biogenesis. Much more complex is that mitochondrial biogenesis exceeds energy demand in WT PGC1αOE heart, where mitophagy is engaged to eliminate excessive mitochondria during young, but impaired mitophagy and subsequently increased oxidative stress worsen the cardiac function of 12-month-old WT PGC1αOE mice (Figure 7).
Aging-induced mitochondrial dysfunction leads to an increase in ROS production and reduced oxidative phosphorylation, thereby decreasing ATP synthesis and cell respiration. Interestingly, mitochondrial function of telomerase deficient (Terc−/−) iPSCs and their differentiated derivatives was severely impaired, while mitochondrial function in Terc−/− ntESCs was considerably improved, with PGC1α a possible target29. Other experimental attempts in different systems, such as tissue-specific overexpression of PGC1α in Drosophila stem and progenitor cells within the digestive tract, extended the life span of this organism30. However, forced expression of PGC1α driven by a cardiac αMHC promoter or an inducible tet-on system in the heart developed cardiomyopathy22, 23, indicating that a fine-tuned expression of PGC1α and relevant downstream signaling molecules is essential for mitochondrial quality control and proper mitochondrial functioning. In our PGC1α knock-in G3 mouse model, we unveiled multiple beneficial aspects of PGC1α induction in the absence of previous documented cardiomyopathy. This difference could be due first to the fact that we used a ROSA26 locus knock-in approach to overexpress mildly one copy of PGC1α; hence, the mild elevation is completely within the physiological range. Second, while the aged G3 heart showed decreased PGC1α expression, the G3 PGC1αOE heart exhibited a PGC1α level comparable to that of WT hearts. In the current study, we did not overexpress two copies of PGC1α in G3 hearts as we were limited by the mating strategy. Further investigation of the dose effect of PGC1α on cardiac function and maximal lifespan in G3 mice would be of great interest.
Given the relatively low mitochondrial dynamics proven in heart31, 32, a logical regulatory hub for the maintenance of its mitochondrial homeostasis lies in the mitophagy, the scavenger of redundant or damaged mitochondria5, 33. Mitophagy is responsible for both coordinating the metabolic reprogramming of heart during maturation34 and for the suppression of aging-associated inflammation through leaking mtDNA-induced cGAS/STING activation35. Several pieces of evidence have implicated that regulation of mitophagy could affect cardiac function and lifespan of the organism. For instance, investigators have reported the salutary effect of natural polyamine spermidine supplement in promoting cardiac performance and extending lifespan in mice via activating mitophagy36. In contrast, ablation of autophagy-related gene leads to cardiomyopathy37, 38. In present study, we saw an elevated mitophagy in WT PGC1αOE heart at 3-month-old but reduced mitophagy at the age of 12-month-old, which coincides with the changes in mitochondrial respiration and cardiac function of WT PGC1αOE mice. Despite we cannot exclude that ROS elevation, contractility alterations related to mitochondrial number expansion, and other possibilities lead to cardiomyopathy in WT PGC1αOE mice, current finding implicates mitophagy may be essential for maintaining the equilibrium of PGC1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and ROS production within a physiological-tolerant range. If so, a well-orchestrated activation of both PGC1α and mitophagy in heart is worth testing in eliminating adverse effects seen in old WT PGC1αOE mice, and possibly in previous cardiac PGC1α overexpression models.
Apart from known regulation of thermogenesis, mitochondrial biogenesis, respiration, fatty acid oxidation, and anti-oxidative effect, mounting studies have implicated that PGC1α may involve other physiological functions39-42. Of note, direct evidence from Tran et al. indicates that PGC1α is capable of driving de novo nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide biosynthesis and therefore enhancing stress resistance43. In line with this, we also documented a restored NAD+ level concurrent with reduced inflammation and protein aggregates in G3 PGC1αOE hearts. This effect is reminiscent of the reduction of protein aggregates and improved cognitive function that occurs with NAD+ supplementation in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease44. These observations warrant further investigation to clarify how NAD+ and PGC1α influence inflammation and proteostasis in the heart.
There are some limitations of the study. First, the goal of this study was to evaluate the dosage effect of PGC1α overexpression in murine models. We cannot exclude the possibility that a different phenotype of PGC1α overexpression would occur in primates and humans. Given that laboratory mice have long telomeres as compared with humans do, it is obligatory to test the biological function of PGC1α overexpression in mice with shorter telomeres in order to extrapolate these findings to human aging. Our study provides the prove of principal that moderately boosting PGC1α level could restore mitochondrial function and thereby rejuvenate the cardiac aging in the presence of short telomeres. Nevertheless, the cause-effect links between telomerase deficiency, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cardiomyopathy require further investigation. We cannot exclude that the cardiomyopathy could be driven by a separate primary process with secondary mitochondrial dysfunction that is partially restored by PGC1α overexpression (thus energetic and functional improvement) versus a direct connection between telomerase function, mitochondrial function, and PGC1α activity. Second, we acknowledge the pitfall in the assessment of cardiac function, including ejection fraction and fractioning shortening that rely on m-mode analysis of the short axis view of echocardiography, depends on geometrical assumptions. Third, our survival study included both male and female animals. Although we did not observe a significant difference between male versus female mice, future investigations should consider the impact of gender on the regulatory effect of PGC1α overexpression on cardiac function and longevity. Finally, a few challenges ahead remain to tackle with, before PGC1a therapy becomes clinical available. For instance, directly upregulate or downregulate the expression of miscellaneous PGC1a may cause a series of biological effects, rather than simply changing the mitochondrial volume and respiration. Therefore, it is mandatory to carefully consider the dose and time period of PGC1a boosting strategy after a comprehensive assessment of the overall mitochondrial fitness (i.e. mitochondrial abundance, quality control, mitophagy capacity, etc.) in order to achieve an optimal clinical translation of the PGC1a therapy.
Taken together, our study suggests that fine-tuning the expression of PGC1α is crucial for the cardiac homeostasis, as the balance between mitochondrial biogenesis and clearance is vital for regulating mitochondrial homeostasis. Given that uncertainty in PGC1α level under various pathological conditions, these results reinforce the importance of carefully evaluating the PGC1α-boosting strategies in a context-dependent manner to facilitate clinical translation of novel cardioprotective therapies.
NOVELTY AND SIGNIFICANCE
What Is Known?
- PGC1α is involved in the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and function.
- Age-associated telomere attrition is linked to cardiac dysfunction, with PGC1α a possible target.
- Attempts to boost PGC1α levels as a therapeutic strategy has had contradictory results.
What New Information Does This Article Contribute?
- Moderate cardiac PGC1α overexpression is sufficient to revitalize mitochondrial and cardiac function in third generation telomerase-deficient (G3) mice.
- However, PGC1α overexpression in telomere-intact mice leads to accelerated cardiac aging and a significantly shortened lifespan.
- The fine-tuning of PGC1α level is crucial for the mitochondrial and cardiac homeostasis partially via the balance between mitochondrial biogenesis and clearance.
Although PGC1α has been studied extensively within the context of energy metabolism and mitochondrial function in the heart, multiple attempts have failed to upregulate PGC1α expression as a therapy.. By using a ROSA26 locus knock-in approach to mildly overexpress PGC1α in cardiomyocytes, we observed the consequences of cardiac PGC1α overexpression in the telomere-intact and telomere dysfunctional mouse models, in which telomerase-deficient heart exhibits a lower basal PGC1α expression in comparison to the telomere-intact counterpart. While WT mice exhibited a relatively consistent PGC1α expression and mitochondrial abundance, overexpression of PGC1α accelerated cardiac degeneration and significantly shortened lifespan in WT mice at least partially due to ROS insult and perturbed mitophagy. By contrast, in hearts of G3 mice which show reduced PGC1α expression with advanced age, cardiac-specific PGC1α knock-in normalized the PGC1α level comparable to that of WT mice and attenuated mitochondrial dysfunction, thereby preserving cardiac performance and extending lifespan. Our study suggests that fine-tuning the expression of PGC1α is crucial for cardiac homeostasis, and synergistic activation of mitophagy in PGC1α-enhancing strategies may have a role in cardioprotective therapies.
Supplementary Material
315529 Online Supplement
315529 Preclinical checklist
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Stephanie C. Tribuna for secretarial assistance, Yaoli Deng and all staffs in the Center of Experimental Animals, Hangzhou Normal University for animal caretaking, Li Wang, Beibei Wang and Ping Yang in the Center of Cyro-Electron Microscopy (CCEM), Zhejiang University for their technical assistance on transmission electron microscopy analyses, Jiabin Lin and Jing Zhao for mouse echocardiography, Qingtao Hu for RNA sequencing data analysis, and all members of the Ju’s lab, particularly Weiwei Yi and Xianda Chen for flow cytometry analysis, and Fan Yang for critical insights and suggestions.
SOURCES OF FUNDING
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91749203, 81525010 and 81420108017) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0103302), Innovative Team Program of Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory (2018GZR110103002) and the Program for Guangdong Introducing Innovative and Entrepreneurial Teams (2017ZT07S347) to Z.J., the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81400221), and Hangzhou Normal University (PF14002004017) to X.Z., and grants from the EPFL, Systems X (SySX.ch 2013/153), the Velux Stiftung (1019), and the Swiss National Science Foundation (31003A-140780) to J.A., and grants from the US National Institutes of Health (HL061795, HG007690, and GM107618), and the American heart Association (D700382) to J.L., the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81771520) and Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (2016C34002) and Health Bureau of Zhejiang Province (2015DTA001) to G.M., and grants from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (17DZ2273200/16DZ2290900).
Nonstandard Abbreviations and Acronyms:
| 3-MA | 3-methyladenine |
| AA | Antimycin A |
| Nppa=gene | Atrial natriuretic peptide |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| bpm | Beats per minute |
| Nppb=gene | B-type natriuretic peptide |
| FCCP | Carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone |
| PGC1αOE | Cardiac-specific PGC1α overexpression |
| G3 PGC1αOE | Cardiac-specific PGC1α knock-in in the third generation of telomerase-deficient mice |
| WT PGC1αOE | Cardiac-specific PGC1α knock-in in wild-type mice |
| EF | Ejection fraction |
| FS | Fractional shortening |
| HW/BW | Heart weight-to-body weight ratio |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IVSd | Interventricular septal end diastole |
| IVSs | Interventricular septal end systole |
| LVIDd | Left ventricular internal diameter end diastole |
| LVIDs | Left ventricular internal diameter end systole |
| LVPWd | Left ventricular posterior wall end diastole |
| LVPWs | Left ventricular posterior wall end systole |
| MFI | Mean fluorescence intensity |
| mtDNA | Mitochondrial desoxyribonucleic acid |
| Myh=gene | Myosin heavy chain |
| nDNA | Nuclear desoxyribonucleic acid |
| Oligo | Oligomycin |
| OCR | Oxygen consumption rate |
| PGC1α=protein; Ppargc1a=gene | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α |
| Rapa | Rapamycin |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| Rot | Rotenone |
| SASP | Senescence-associated secretory phenotype |
| Tg | Thapsigargin |
| G3Terc−/− | Third generation of telomerase-deficient mice |
| WT | Wild type |